
As a business law student, you might have questioned the differences between corporate law and business law, as the line between the two is quite vague. Being a subset of business law in itself, corporate law definitely has the characteristics of business law; however, it does have specific, subtle differences. Students fail to understand this difference, feeling helpless about addressing the topics.
Here, we have elaborated on such differences and the types of business law assignments v/s corporate law assignments to understand the subtleties. As a law assignment writing help platform, you can also contact Quick Assignment Hub to get help with business law and corporate law assignments to boost your grades.
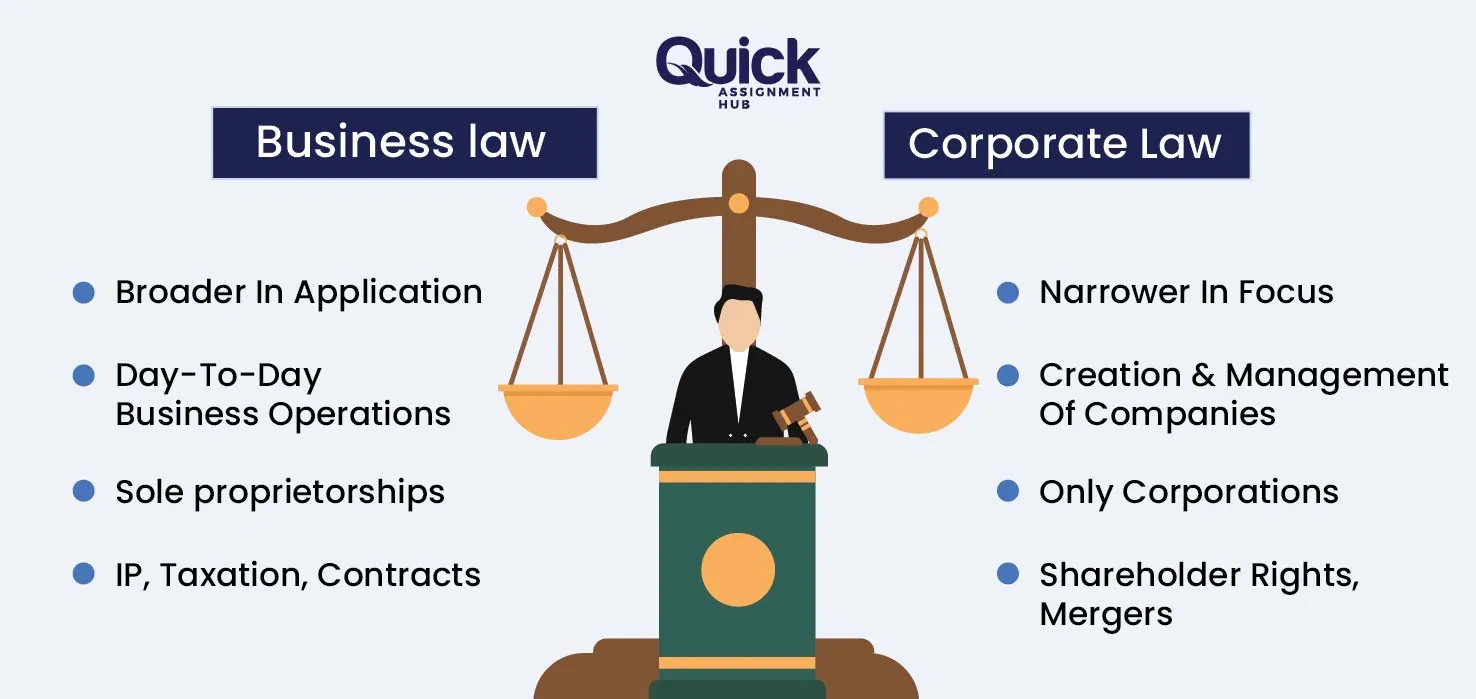
Business and corporate law are popular legal specialisations for higher education in the UK. As the name suggests, business law regulates and governs commercial business transactions, mainly including legal principles and statutes on how businesses must operate. It focuses on the key areas like contract law, intellectual property rights, and legal aspects of employment and strives to protect the parties' rights.
Corporate law, also popularly known as the company law, outlines the critical legal frameworks and rules for businesses and companies. From the very establishment of the company to its closure, it looks after areas like business compliance, shareholder rights, responsibilities of the board of directors, etc. Corporate law comes under business law only; however, it is more specific, whereas business law is broader and diverse.
Also read: Understanding Academic Misconduct and Strategies to Prevent It
In law programs, you often come across cross-disciplinary topics for assignments, and one of the common areas of confusion is between business and corporate law. Here, we have listed the differences between business law and corporate law, so you can get profound clarity on how to address your assignment better:
The core concern of business law is providing a proper framework to promote fairness, accountability, and transparency in business functions and operations. This framework outlines how businesses must be established and operated, highlighting the rights and responsibilities of the parties involved. Some critical areas it covers are:
Legal agreements and unnecessary contracts
Commercial interactions and interests of the parties
Fair compensation and employee benefits
Defends stakeholders rights
Protection of consumers from fraudulent companies
In the comparative study of corporate and business law, the scope of business law is wider, covering extensive legal areas. From the very scope of the formation and the dissolution of the establishments to interpreting the agreement between parties and even company closure, everything comes under its purview. To understand the scope better, learn about the areas that it touches:
Establishment of various business entities, outlining the operations and governance policy.
Create and interpret important agreements to ensure the contracts are legally binding for the stakeholders involved.
It aims to protect trademarks and business innovations under the purview of intellectual property rights and consumer rights.
In the UK, business law encompasses business entities, limited companies, LLPs, public and private limited companies, sole proprietorships, and partnerships. It also includes charitable organisations that operate under the Companies Act of 2006 in the UK. Other involved parties include the investors, business owners, employees, legal advisors, etc.
The business laws in the UK are primarily regulated by statutes, most notably the Companies Act 2006, the Consumer Rights Act 2015, and various other case laws. Most public companies in the UK are under the framework of the UK Corporate Governance Code, which covers aspects of consumer rights, legal penalties, etc.
There are many examples of business laws, like contract law, employment law, consumer protection laws, IP law, etc. An example of contract law can be when any company fails to deliver the services agreed upon in the contract; as per the business contract law, the party can seek legal help for damages or fraud.
One main difference between business law and corporate law can be their core concerns and issues. Corporate law is mainly concerned with the operation, primarily the dissolution, of companies, and governmental relationships between stakeholders. The other vital areas it covers are:
Creating the ownership structure of the companies and setting the main rules for the company establishment.
It also checks on the duties and core responsibilities of the stakeholders and the board of directors involved.
Lays down clear and transparent disclosure of the financial information, agreements and corporate activities to determine accountability.
Ensure that ethical compliance is maintained, and set that standard for all bind companies.
Ethical compliance, business law and corporate law appear more or less the same; the scope, like the concerns, also differs between the corporate and business laws. As a subset of business law, corporate law's scope is narrower than that of business law. Business law deals with more generic issues. To understand the slight difference between business law and corporate law, check the scope of corporate law here:
The scope of corporate law is limited to corporations, advising on corporate governance, ensuring high regulatory compliance, etc.
It handles mergers and acquisitions, looks after the legal aspects of partnerships, takeovers, critical joint ventures, and more.
Another significant scope of corporate law is the critical drafting, reviewing and negotiating various business contracts to protect company interests.
Corporate laws deal with the main business entities like the public limited companies, limited liability partnerships, and private limited companies. Corporate law also encompasses the CIC or community interest companies, which are the UK's social enterprises.
The UK's business and corporate law are primarily regulated by the Companies Act 2006 and other legislation, such as the Economic Crime and Corporate Transparency Act of 2023. Regarding financial difficulties, the key legislation is the Insolvency Act of 1986 in the UK.
When companies and business organisations want to trade publicly or get listed in the stock market, they must comply with the corporate law. Corporate law lays down the rules to navigate registration and even disclosure requirements.
While attempting the law assignments, you also need to remember the differences and similarities between business and corporate law. For different types of legal analysis and specific legal citations, you can even get assignment expert help to overcome the confusion between business law assignments and corporate law assignments. Let's see the common types of assignments of these two specialisations:
Learn more about: Trending Topics For 2025 To Ace Your Law Assignment
Any hypothetical legal dispute in business, requiring the application of principles and statutes
Drafting hypothetical contracts and agreements, and analysing them.
Presentation on reviewing any court cases or legislation.
Conducting a detailed study on corporate social responsibility and insolvency matters.
Comparative law assignments between Tort law and the jurisdictions of other countries, like India and USA.
Practical assignments based on problem-solving that involve analysing compliance issues and corporate restructuring.
By now, you can understand that the common similarity between business law and corporate law concerns business activities. While business law is more general and has wider specialisation, corporate law is a more specialised area that focuses more on corporate governance. The above-mentioned difference between business and corporate law will clear your doubts and confusion. However, if you are looking for professional law assignment help in both specialisations, Quick Assignment Hub is the best platform. We cover everything from legal citation help in OSCOLA to well-analysis and evidence-based analysis. Place your order today and skyrocket your Law grades.